Zebrafish gRNA design for CRISPR
I chose to use the Wente-Chen design which showed excellent results even with multiplexed targeting:
You can order the plasmids from Addgene.
gRNA design
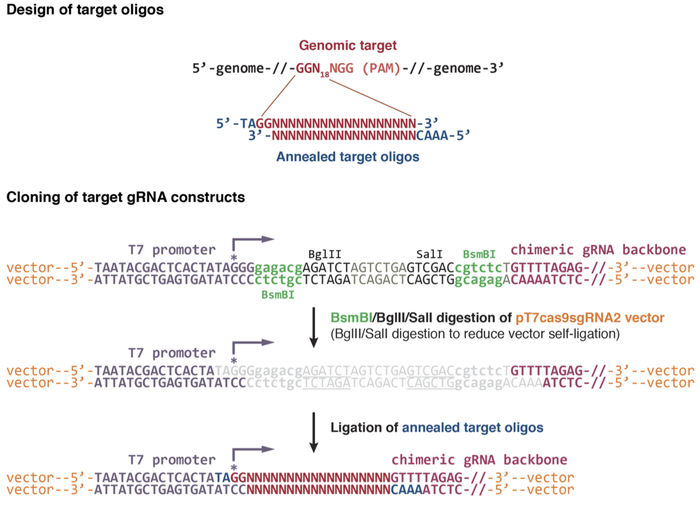
Target region should obey the following pattern: GG-N(19)-GG.
Tools
Dos & don’ts (probably incomplete)
- Pick 2-3 distinct targets;
- Select exons upstream rather than downstream on the gene;
- Have these targets preferentially in several exons;
- Avoid repetitive sequences;
- Design several target sequences at once, even if not ordering all oligos initially.
Using ChopChop
Get matrix with Target sequence and its annotations.
While at this take notice of one primer pair to amplify the targeted region.
Design oligos
To design oligos based on the target sequence, one must remove the PAM sequence (this will be in the genome) and add sequences to the ends of the primers so that after annealed, they can complement the pattern of the digested plasmid.
For the Wente-Chen design, these are “TA” to the left primer and “AAAC” to the right one.
This small Python script does the job:
import pandas as pd
from Bio import Seq
df = pd.read_csv("gRNA_design.csv")
df["left_oligo"] = None
df["right_oligo"] = None
for i in range(len(df)):
target = str(df.ix[i]["target_sequence"])
df.loc[i, "left_oligo"] = "TA" + target[:20] # add 5' seq to 20 nt-long RNA
df.loc[i, "right_oligo"] = "AAAC" + Seq.Seq(target[:20]).reverse_complement()[:18] # add restriction site and take PAM seq out
df.to_csv("gRNA_design.primers.csv", index=False)Cloning
As described here:
Plasmids
- pCS2-nCas9n - zf codon-optimized Cas9 with nuclear localization signals
- pT7-gRNA - gRNA backbone
Reagents, materials
- BsmBI, BglII, SalI, BamHI and NotI or XbaI restriction enzymes
- T4 ligase
- Proteinase K
- MEGAshortscript T7 kit (Ambion/Invitrogen)
- mMESSAGE mMACHINE SP6 or T3 kit (Invitrogen)
- RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen)
- mirVana miRNA Isolation Kit (Ambion/Invitrogen)
- NEB Buffer 1, 3
- T4 ligase buffer
- LB/amp plates
Literature
- Ablain, J., Durand, E. M., Yang, S., Zhou, Y. & Zon, L. I. A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish. Dev. Cell 32, 756–764 (2015).
- Auer, T. O., Duroure, K., Cian, A. De, Concordet, J. & Bene, F. Del. homology-independent DNA repair Highly efficient CRISPR / Cas9-mediated knock-in in zebrafish by homology-independent DNA repair. 142–153 (2014). doi:10.1101/gr.161638.113
- Gagnon, J. a. et al. Efficient mutagenesis by Cas9 protein-mediated oligonucleotide insertion and large-scale assessment of single-guide RNAs. PLoS One 9, 5–12 (2014).
- Hruscha, A. et al. Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing with low off-target effects in zebrafish. Development 140, 4982–7 (2013).
- Hwang, W. Y. et al. Efficient genome editing in zebrafish using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 227–9 (2013).
- Hwang, W. Y. et al. Heritable and Precise Zebrafish Genome Editing Using a CRISPR-Cas System. PLoS One 8, 1–9 (2013).
- Jao, L.-E., Wente, S. R. & Chen, W. Efficient multiplex biallelic zebrafish genome editing using a CRISPR nuclease system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 13904–9 (2013).
- Kimura, Y., Hisano, Y., Kawahara, A. & Higashijima, S. Efficient generation of knock-in transgenic zebrafish carrying reporter/driver genes by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome engineering. Sci. Rep. 4, 6545 (2014).
- Shen, B. et al. Generation of gene-modified mice via Cas9/RNA-mediated gene targeting. Cell Res. 23, 720–3 (2013).